Overdose Deaths – A National and World Epidemic
190,000 people worldwide die from drugs-related deaths, predominantly related to opioid overdose.
- Drug overdose is the leading cause of injury-related deaths, greater than car accidents and homicide
- Opioids—prescription pain relievers, heroin and synthetic opioid fentanyl—are the main driver of overdose deaths
- 63,600 Americans died from drug overdoses in 2016
- Opioids account for more than 66% of all overdose deaths – killing more than 42,000 people in 2016
Sources: SAMSHA 2014 National Survey on Drug Use, CDC Drug Overdose Data, and Health and the World Drug Report 2015
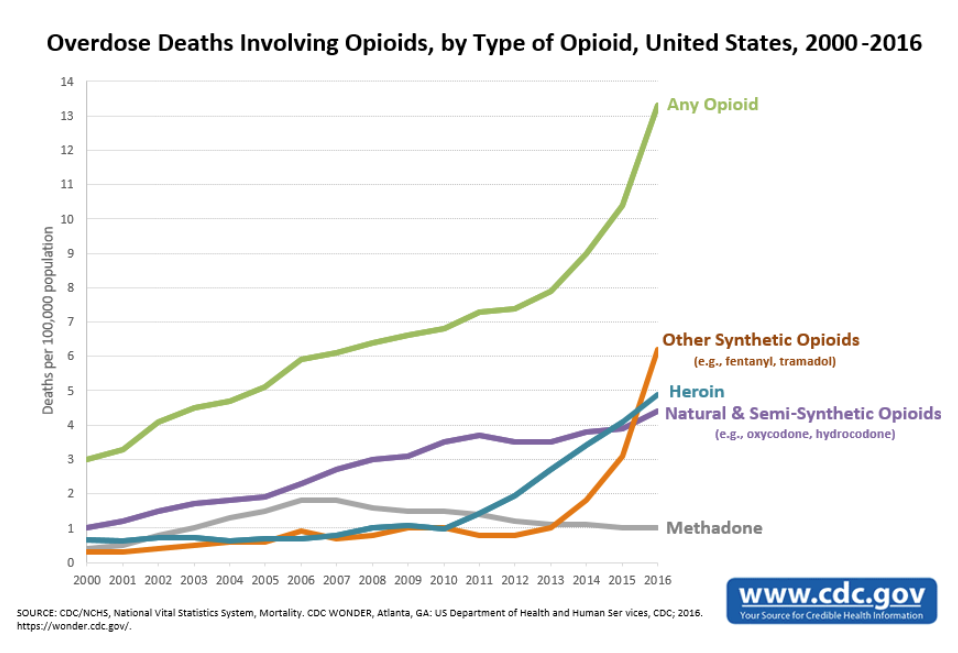
Opioids Represent 66% of All Overdose Deaths
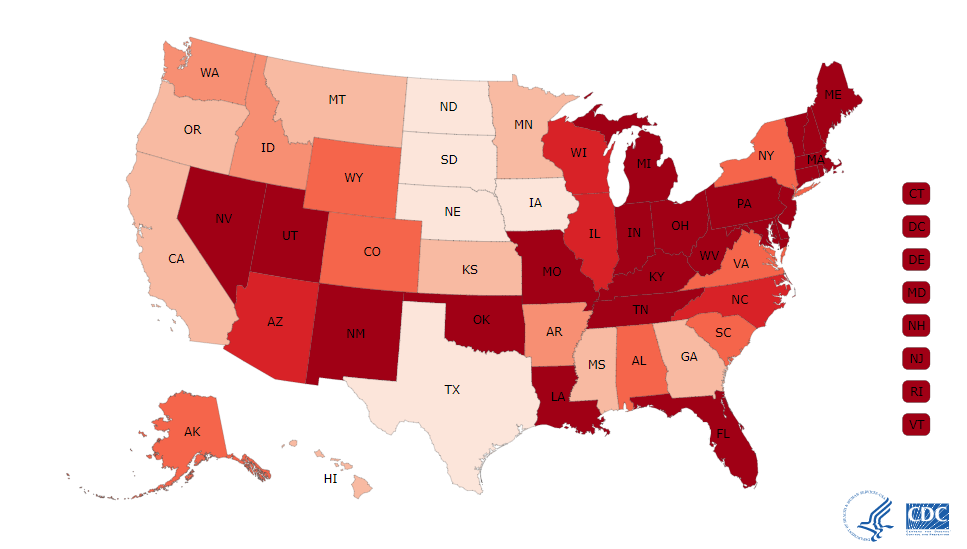
Drug overdose is the leading cause of accidental death in the United States. Killing more people than car accidents and guns – more than 63,600 Americans died from drug overdoses in 2016. In fact overdose is the leading cause of death for Americans under 50.
Of the 63,600 reported overdose deaths – Opioids killed 42,249 people in 2016 – representing 66% of all overdose deaths. There is a growing body of evidence to suggest that opioid overdose deaths are under-reported. One fifth to one quarter of death certificates do not identify a specific drug. This results in underestimating the involved drug and additional errors when measuring rates across time.
Provisional data for 2017 from the CDC show no signs of the epidemic slowing down, with an estimate of more than 66,000 overdose deaths for the year with more state reporting due.
Source: CDC www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/data/